The 2024 G20 Summit in Brazil brought global leaders together in Rio de Janeiro to discuss urgent challenges. From addressing climate concerns to humanitarian aid and global reforms, this event focused on decisions and agreements that may shape the future of international cooperation.
This article examines the outcomes and their potential impact on global policies.
| Location | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil |
| Dates | November 18–19, 2024 |
| Participants | Leaders of G20 nations, invited guests, and representatives from international organizations |
| Key Topics | Humanitarian aid, climate goals, global hunger, poverty reduction, and UN reforms |
| Major Outcomes | – A call for ceasefires in conflict zones – Initiative to combat global hunger and poverty – Reaffirmation of climate goals to limit warming to 1.5°C – Proposal for billionaire tax to address inequality – Push for reforms in global governance |
| Notable Contributions | – Spain pledged €400 million to aid the poorest nations – Increased focus on sustainable development |
Key Participants and Nations Involved

| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| G20 Member Nations | Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom, United States, European Union |
| Guest Nations | Spain, Singapore, United Arab Emirates, Nigeria |
| International Organizations | United Nations, International Monetary Fund, World Bank, World Trade Organization |
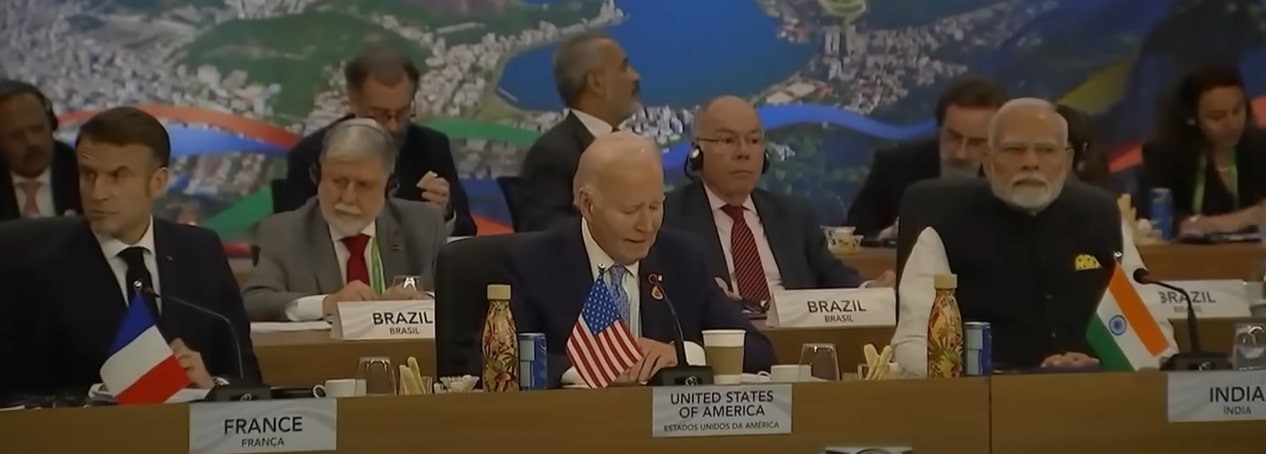
The summit brought together influential leaders, including:
- Joe Biden from the United States
- Xi Jinping from China
- Narendra Modi from India
- Olaf Scholz from Germany
- Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, the host leader from Brazil
- Emmanuel Macron from France
- Fumio Kishida from Japan
- Rishi Sunak from the United Kingdom
- Mohammed bin Salman from Saudi Arabia
- Cyril Ramaphosa from South Africa
- Recep Tayyip Erdoğan from Turkey
- Justin Trudeau from Canada
- Sergey Lavrov representing Russia (in place of Vladimir Putin)
- Anthony Albanese from Australia
- Alberto Fernández from Argentina
- Joko Widodo from Indonesia
- Giorgia Meloni from Italy
- Andrés Manuel López Obrador from Mexico
- Yoon Suk Yeol from South Korea
- Charles Michel and Ursula von der Leyen representing the European Union
- Pedro Sánchez from Spain
- Lee Hsien Loong from Singapore
- Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan from the United Arab Emirates
- Bola Ahmed Tinubu from Nigeria
Guest nations such as Spain and Singapore added unique perspectives to the discussions. These countries often bridge regional and global economic policies, highlighting the significance of inclusive dialogue.
US President Joe Biden, Canadian PM Justin Trudeau, and Italian PM Giorgia Meloni missed the G20 group photo.
After a bilateral meeting, they arrived too late, as the other leaders had already left without waiting for them.#G20Brasil2024 #G20RiodeJaneiro pic.twitter.com/94nkE2U7kI
— 鳳凰資訊 PhoenixTV News (@PhoenixTV_News) November 19, 2024
Main Agenda and Topics Discussed
| Humanitarian Aid | Support for regions impacted by conflict, including Gaza and Ukraine |
| Climate Goals | Reaffirmation of limiting global warming to 1.5°C and energy transition strategies |
| Global Hunger and Poverty | Launch of initiatives to address hunger and reduce poverty through international efforts |
| Economic Reforms | Proposal for a global billionaire tax to reduce inequality |
| UN Security Council Reform | Discussions on restructuring to reflect modern global dynamics |
Addressing Humanitarian Crises
One of the most pressing topics was the growing humanitarian needs in conflict zones. Leaders emphasized the importance of ceasefires and coordinated international efforts to provide aid to areas like Gaza and Ukraine. The G20 Summit had a strong focus on finding a real solution to stop the wars in Gaza and Ukraine.
Climate Action and Energy Transition
The commitment to limiting global warming to 1.5°C was reaffirmed, with discussions focusing on practical steps toward energy transitions that benefit all economies. These plans aim to balance environmental priorities with sustainable development. Brazil is also showing commitment by investing in new technologies, such as the latest air pollution monitoring system.
Tackling Hunger and Poverty
A new initiative led by Brazil aimed to confront global hunger and poverty. The discussions highlighted the political and economic factors contributing to these issues, moving beyond outdated narratives of natural scarcity.
The Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty is officially launched! This important legacy of the Brazilian presidency of the G20 seeks to guarantee the right to food for all citizens of the world. United, we can build a less unequal world!
🎥 Audiovisual/PR pic.twitter.com/dC4qQKcREE
— G20 Brasil (@g20org) November 18, 2024
Pushing for Economic Equality
The G20 summit included a controversial proposal for a global billionaire tax. While the idea garnered mixed reactions, it underscored the need to address the widening wealth gap across nations.
📢 Today, Brasil’s Finance Minister Fernando Haddad announced a historic consensus at the G20 on international taxation, including the taxation of large fortunes. 💼💰 The agreement was reached during the 3rd meeting of G20 Finance Ministers. pic.twitter.com/xVukoXXUrF
— G20 Brasil (@g20org) July 25, 2024
Revisiting Global Governance
Calls for reforming the United Nations Security Council reflected a growing consensus that current structures no longer represent the realities of the modern world. The focus was on creating a more inclusive and effective system.
Climate Goals and Energy Transition Plans
Sustainability, climate change, and a just transition were the topics of the second plenary session at the Social G20 Summit this Friday (15th). pic.twitter.com/2ZbqUsL6ID
— G20 Brasil (@g20org) November 15, 2024
Leaders acknowledged that without immediate and coordinated action, the environmental and economic consequences could become irreversible.
The discussions included strategies for achieving a global energy transition. A key focus was on reducing reliance on fossil fuels and increasing investment in renewable energy sources. While some member nations pledged to accelerate their transition timelines, others stressed the need for financial and technical support to meet their targets. Developing countries, in particular, emphasized the importance of equitable resource distribution to ensure that energy transitions do not widen global inequality.
A major outcome of the summit involved new commitments to phase out coal power, though no definitive timelines were agreed upon. The lack of a binding agreement highlighted the persistent challenges in balancing national interests with global climate objectives.
The summit also addressed the financial aspect of climate action. Leaders discussed increasing contributions to the Green Climate Fund, a key mechanism for supporting developing nations in adapting to climate impacts and building sustainable energy systems. Wealthier nations were urged to meet their financial commitments, while developing nations emphasized the need for transparency and accountability in fund allocation.
Global Hunger and Poverty Initiatives
Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva introduced the Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty, calling it a critical step toward lifting at least 600 million people out of poverty by 2030. This initiative gained support from 82 countries, 26 international organizations, and several financial institutions and philanthropic groups. Also, that was the key topic of the G20 Summit
Brazil’s President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva opened the summit of the Group of 20 major economies with the launch of a global alliance to combat poverty and hunger that more than 80 countries have agreed to back https://t.co/4JlLupfV5C pic.twitter.com/HzV2yb4cqG
— Reuters (@Reuters) November 18, 2024
Spain’s Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez announced an increased contribution of €400 million to the World Bank’s International Development Association. This commitment marked a 40% rise in Spain’s previous contributions and aimed to strengthen aid to the world’s poorest regions.
Nigerian President Bola Tinubu endorsed the alliance, emphasizing the need to reform the global tax system. He argued that current imbalances hinder sustainable development in low-income countries, making international reforms essential.
Proposals for Economic Reforms and Taxation
The 2024 G20 Summit in Rio de Janeiro brought global economic inequality into focus. One of the most debated topics was a proposal for a global tax on billionaires. This initiative aimed to address the widening wealth gap by introducing a 2% annual tax on the world’s wealthiest individuals. While this idea received support from several nations, it also sparked disagreements about its implementation and potential impact on global investments.
French President Emmanuel Macron voiced strong backing for the billionaire tax, stating that it represents a necessary step toward reducing inequality and funding sustainable development projects. Brazil’s President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva echoed this sentiment, emphasizing the political will needed to overcome resistance from wealthier nations.
The United States, represented by President Joe Biden, expressed cautious support for addressing inequality but highlighted concerns about how such a tax would affect global financial markets. Meanwhile, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz called for a balanced approach that considers the economic stability of all nations while pursuing reforms.
Beyond the billionaire tax, leaders also discussed broader economic reforms. Topics included enhancing international tax transparency to prevent illicit financial flows and increasing support for underdeveloped nations through targeted investments. Developing nations, including Nigeria, stressed the need for fairer global trade policies that enable them to compete on an equal footing.
While the summit highlighted a shared recognition of the inequality challenge, concrete agreements remained limited.
Discussions on UN Security Council Reform
Check out the remarks by João Paulo Capobianco, Executive Secretary of the Ministry of the Environment, at the launch of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal 18, focused on ethnic and racial equality, and the guidebook “Agenda 2030 and the SDGs Within Your Reach,” this Friday. pic.twitter.com/KNF99mcmw8
— G20 Brasil (@g20org) November 15, 2024
Leaders acknowledged the need for changes that address regional imbalances and enhance representation for areas like Africa and Latin America.
Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva argued that the current structure limits the voices of underrepresented regions, calling for reforms to make the council more inclusive. India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted the urgency of ensuring that developing nations have a greater role in decision-making processes.
United States President Joe Biden supported expanding permanent membership to include African nations, while German Chancellor Olaf Scholz made a case for Germany’s inclusion, pointing to the country’s global contributions. Discussions also included addressing concerns raised by nations such as China and Russia, which emphasized the importance of preserving the council’s balance and operational efficiency during any reform process.
The debates showcased a range of perspectives on how best to adapt the Security Council to modern challenges. While there was agreement on the need for reform, opinions diverged on the scope and implementation of proposed changes.
Final Outcomes and Global Impact of the Summit

- The 2024 G20 Summit in Rio de Janeiro concluded with several agreements and declarations aimed at addressing global challenges. Although some issues remain unresolved, the event marked progress on key priorities and set the stage for future action.
- The summit highlighted the importance of addressing humanitarian crises, particularly in Gaza and Ukraine. Leaders called for increased international aid and urged all parties involved to prioritize civilian safety and access to essential resources.
- The reaffirmation of limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius was a central achievement. Nations discussed energy transition strategies and emphasized the importance of fulfilling financial commitments to climate funds, particularly for developing countries.
- Led by Brazil, the newly launched Global Alliance Against Hunger and Poverty received widespread support.
- Although the proposal for a billionaire tax sparked extensive debate, it underscored the growing recognition of global inequality as a pressing issue.
- While no concrete agreement was reached, the summit brought renewed attention to the need for reforms in the United Nations Security Council.
- The Summit resulted in various agreements between countries, including a significant trade pact expanding agricultural exports from Brazil to China.
A few days after the event, there is a smaller gathering focused on women in business. Be sure to check it out.