Military strength shapes global power. Some nations remain at the top. Others have advanced with sharp focus and force. Each one has earned its place through weapons, training, and unmatched discipline. Strongest armies do not rise by chance. They rise through control and command.
Here is the 2025 list of the strongest armies in the world.
Here is the Latest Ranking of Strongest Armies
| Rank | Country | Power Index |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 United States | 0.0699 |
| 2 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 0.0702 |
| 3 | 🇨🇳 China | 0.0706 |
| 4 | 🇮🇳 India | 0.1023 |
| 5 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | 0.1416 |
| 6 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 0.1443 |
| 7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 0.1601 |
| 8 | 🇹🇷 Turkey | 0.1697 |
| 9 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 0.1711 |
| 10 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.1863 |
| 11 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.1878 |
| 12 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 0.1944 |
| 13 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 0.2251 |
| 14 | 🇮🇷 Iran | 0.2269 |
| 15 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 0.2283 |
| 16 | 🇦🇺 Australia | 0.2515 |
| 17 | 🇮🇱 Israel | 0.2596 |
| 18 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 0.2598 |
| 19 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 0.2847 |
| 20 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 0.2882 |
| 21 | 🇵🇱 Poland | 0.2917 |
| 22 | 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 0.3158 |
| 23 | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 0.3235 |
| 24 | 🇹🇼 Taiwan | 0.3302 |
| 25 | 🇹🇭 Thailand | 0.3389 |
| 26 | 🇩🇿 Algeria | 0.3589 |
| 27 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 0.3813 |
| 28 | 🇦🇷 Argentina | 0.3823 |
| 29 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 0.4009 |
| 30 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 0.4087 |
| 31 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 0.4274 |
| 32 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 0.4349 |
| 33 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.4632 |
| 34 | 🇵🇭 Philippines | 0.4691 |
| 35 | 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 0.5251 |
| 36 | 🇰🇵 North Korea | 0.5313 |
| 37 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 0.5419 |
| 38 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 0.5609 |
| 39 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 0.5619 |
| 40 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 0.5644 |
| 41 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 0.5664 |
| 42 | 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 0.5992 |
| 43 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 0.6097 |
| 44 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 0.7347 |
| 45 | 🇮🇶 Iraq | 0.7441 |
| 46 | 🇨🇿 Czechia | 0.7706 |
| 47 | 🇷🇴 Romania | 0.7712 |
| 48 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 0.7743 |
| 49 | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 0.7938 |
| 50 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 0.7967 |
| 51 | 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | 0.8083 |
| 52 | 🇨🇱 Chile | 0.8128 |
| 53 | 🇵🇪 Peru | 0.8475 |
| 54 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | 0.8478 |
| 55 | 🇦🇴 Angola | 0.8702 |
| 56 | 🇷🇸 Serbia | 0.9038 |
| 57 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 0.9447 |
| 58 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 0.9495 |
| 59 | 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | 0.9934 |
| 60 | 🇸🇾 Syria | 1.0026 |
| 61 | 🇲🇦 Morocco | 1.0081 |
| 62 | 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 1.0132 |
| 63 | 🇶🇦 Qatar | 1.0789 |
| 64 | 🇧🇾 Belarus | 1.0901 |
| 65 | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 1.1069 |
| 66 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 1.1333 |
| 67 | 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 1.1844 |
| 68 | 🇨🇺 Cuba | 1.1869 |
| 69 | 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 1.1891 |
| 70 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1.2064 |
| 71 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 1.2351 |
| 72 | 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 1.2388 |
| 73 | 🇨🇩 Democratic Republic of the Congo | 1.2491 |
| 74 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | 1.2881 |
| 75 | 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | 1.3459 |
| 76 | 🇸🇩 Sudan | 1.4119 |
| 77 | 🇰🇼 Kuwait | 1.4261 |
| 78 | 🇴🇲 Oman | 1.4448 |
| 79 | 🇱🇾 Libya | 1.4449 |
| 80 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | 1.4651 |
| 81 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | 1.4692 |
| 82 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | 1.4851 |
| 83 | 🇹🇲 Turkmenistan | 1.4906 |
| 84 | 🇬🇪 Georgia | 1.6969 |
| 85 | 🇵🇾 Paraguay | 1.7053 |
| 86 | 🇧🇭 Bahrain | 1.7163 |
| 87 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | 1.7237 |
| 88 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 1.7395 |
| 89 | 🇰🇪 Kenya | 1.7629 |
| 90 | 🇦🇱 Albania | 1.8188 |
| 91 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 1.8286 |
| 92 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | 1.8377 |
| 93 | 🇹🇩 Chad | 1.8607 |
| 94 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 1.8779 |
| 95 | 🇭🇳 Honduras | 1.9629 |
| 96 | 🇺🇾 Uruguay | 1.9695 |
| 97 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | 1.9851 |
| 98 | 🇨🇮 Ivory Coast | 1.9869 |
| 99 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 1.9911 |
| 100 | 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | 2.0057 |
1. United States

The United States holds the strongest military position in 2025, backed by unmatched resources and advanced capabilities.
The US has kept the leading position among the strongest armies for quite a long time, but there are serious followers.
- Largest Defense Budget – At $831 billion, the U.S. has the highest defense budget worldwide.
- Global Reach – Bases in over 70 countries, providing rapid deployment options.
- High-Tech Arsenal – Cutting-edge technology, including stealth fighters and nuclear-powered carriers.
Latest update about their military development is the plan of US President Donald Trump to build the Iron Dome in America similar to one in Israel.
| Defense Budget | $831 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 2,127,500 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 13,300 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Aircraft Carriers | 11 active |
| Warships | 92, including destroyers |
| Submarines | 68 |
| Active Tanks | 6,612 |
| Missile Defense Systems | THAAD, Aegis, and more |
2. Russia

Russia ranks second in 2025 military strength, backed by extensive resources and a powerful nuclear arsenal.
The situation remains unchanged for decades when it comes to top 2 strongest armies.
- Significant Defense Budget – Russia’s defense spending reaches $109 billion.
- Global Military Influence – Despite challenges, Russia maintains a powerful presence, particularly in Eastern Europe.
- Advanced Arsenal – High-tech aircraft and a robust submarine fleet enhance Russia’s defense capabilities.
| Defense Budget | $109 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 3,570,000 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 4,100 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | Over 200, including destroyers and frigates |
| Submarines | 70, including nuclear-powered models |
| Active Tanks | 12,420, a high tank count globally |
| Missile Systems | S-400 and other advanced defense systems |
3. China

China ranks third in global military power for 2025, leveraging its large population and advanced technology to create a formidable force.
China stands as a serious contender for the top spot on the list of strongest armies, with rapid advancements in technology, expanding military budgets, and strategic global influence.
- High Defense Budget – China’s defense budget is around $227 billion, the second-largest globally.
- Regional Dominance – China’s military power secures its influence across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Technological Development – Advances in missile technology, cyber capabilities, and AI integration.
| Defense Budget | $227 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 3,170,000 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 3,285 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | 50, including destroyers and frigates |
| Submarines | 78, including nuclear-powered models |
| Active Tanks | 5,250 |
| Missile Systems | Extensive missile arsenal, including DF-41 ICBMs |
4. India

India holds the fourth position in military strength in 2025, building on a vast population, strategic investments, and a strong nuclear deterrent.
Focus on modernization and regional security places it among the top military powers.
There are many positive trends showing that India will keep the top spot of strongest armies in the future, and even aim for the first place.
- Growing Defense Budget – India’s budget stands at $74 billion, supporting continuous modernization.
- Significant Manpower – India benefits from one of the largest active and reserve forces globally.
- Strategic Nuclear Capabilities – India maintains a reliable nuclear arsenal for deterrence.
| Defense Budget | $74 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 5,137,550 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 2,100 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | 35, including destroyers and frigates |
| Submarines | 17, including nuclear-capable models |
| Active Tanks | 4,730 |
| Missile Systems | Agni and Prithvi series for regional deterrence |
5. South Korea

South Korea ranks fifth in 2025, maintaining strong military capabilities focused on advanced technology and defense readiness.
With a significant defense budget, South Korea stands prepared for any regional threats.
The biggest treat for them is their northern neighbor, North Korea, which is the mean reason why they are investing in military equipment with focus on staying among the top of strongest armies in the world.
- Focused Defense Budget – South Korea’s $44.7 billion budget supports advanced weapons and technology.
- Defense Against Regional Threats – Positioned near North Korea, South Korea’s military emphasizes readiness and technology.
- Advanced Missile Defense – High-tech systems protect against regional ballistic threats.
| Defense Budget | $44.7 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 3,820,000 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 1,600 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | 30, including destroyers and frigates |
| Submarines | 22, primarily diesel-electric |
| Active Tanks | 2,614 |
| Missile Defense Systems | THAAD and Indigenous systems |
6. United Kingdom

The United Kingdom ranks sixth in global military power for 2025, with a solid foundation in defense spending, advanced technology, and strong international alliances.
- Significant Defense Budget – The UK’s defense budget stands at $62.8 billion.
- Strong Naval Presence – Two active aircraft carriers and a robust fleet.
- Nuclear Deterrent – Strategic nuclear arsenal bolsters defense capability.
| Defense Budget | $62.8 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 1,108,860 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 1,200 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Aircraft Carriers | 2 active carriers |
| Warships | 36, including destroyers and frigates |
| Submarines | 10, including nuclear submarines |
| Active Tanks | 227 |
| Missile Systems | Advanced cruise and ballistic missiles |
7. Japan
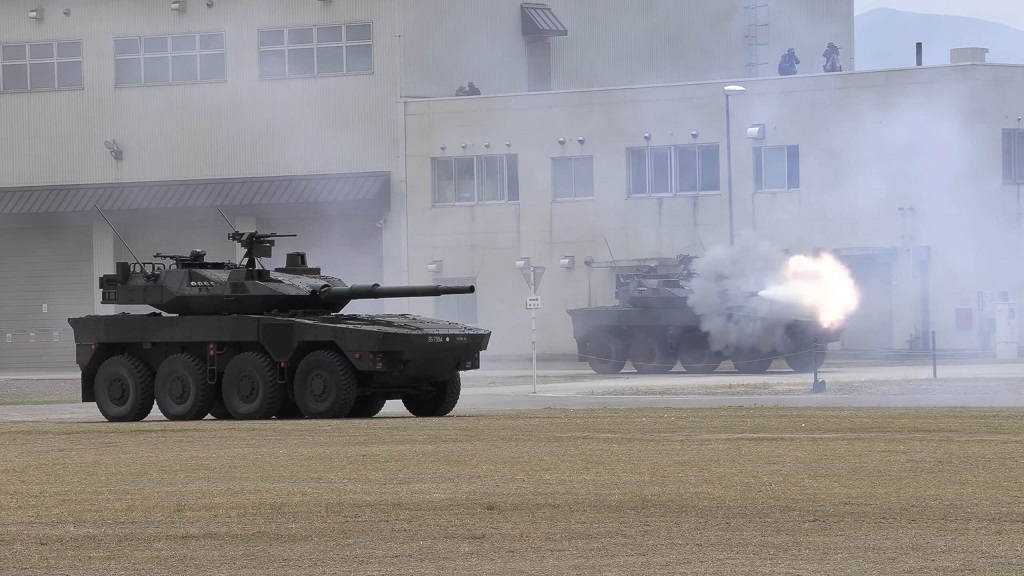

Japan ranks seventh in 2025, focusing heavily on advanced technology and regional security.
Despite constitutional restrictions, Japan has a strong self-defense force capable of significant power projection.
- Advanced Technology – Japan’s military emphasizes cutting-edge tech and weaponry.
- Defense-Oriented Strategy – Focused on defense and regional security in Asia.
- Notable Naval Force – Japan operates a capable fleet, including destroyers and helicopter carriers.
| Defense Budget | $53 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 328,150 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 1,450 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | 45, including destroyers and helicopter carriers |
| Submarines | 20 |
| Active Tanks | 1,004 |
| Missile Systems | Advanced air-to-air and anti-ship missiles |
8. Turkey
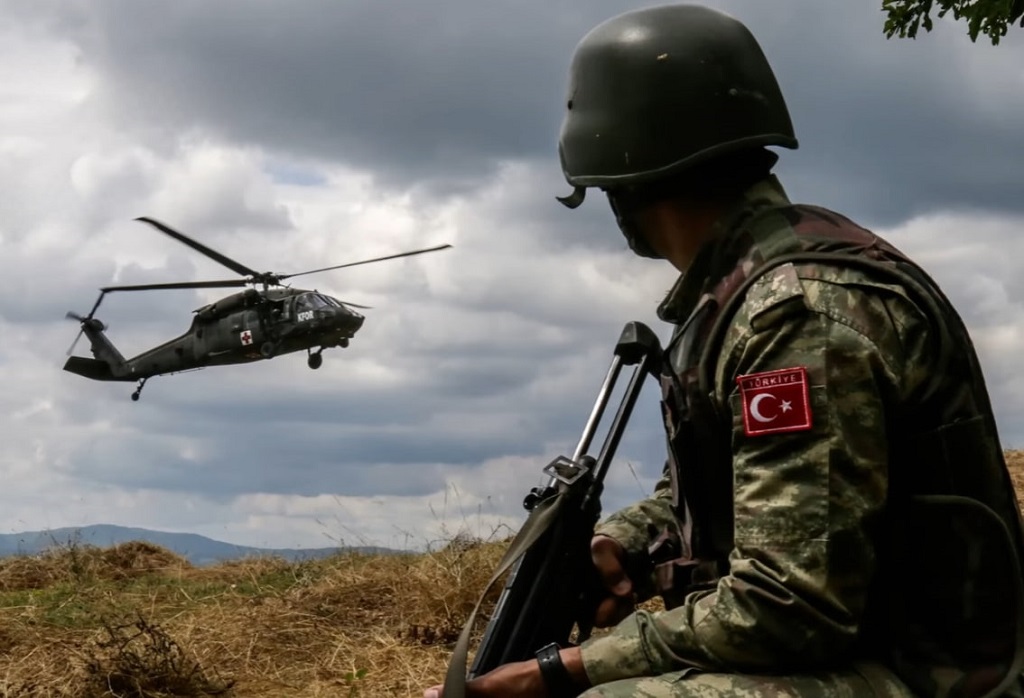

Turkey ranks eighth in military strength, with a focus on regional influence and self-sufficiency in defense production.
Its position as a NATO member and its active military industry contribute to its strength.
- Growing Defense Budget – $40 billion.
- Regional Influence – Strategic positioning gives it significant regional power.
- Self-Sufficient Production – The country invests heavily in its own defense technology and equipment.
| Defense Budget | $40 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 883,900 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 1,067 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | 26, including frigates and submarines |
| Submarines | 12 |
| Active Tanks | 3,045 |
| Missile Systems | Indigenous air defense systems |
9. Pakistan
Pakistan ranks ninth, emphasizing strategic depth and nuclear deterrence.
The military strength is primarily focused on defending its borders and maintaining regional stability.
- Balanced Defense Budget – Defense spending stands at $6.3 billion.
- Strong Land Forces – Large armored fleet and experienced ground personnel.
- Nuclear Deterrent – Key element of Pakistan’s defense strategy.
| Defense Budget | $6.3 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 1,704,000 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 1,372 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Warships | 20, including destroyers and submarines |
| Submarines | 9 |
| Active Tanks | 2,680 |
| Missile Systems | Ballistic and cruise missiles |
10. Italy
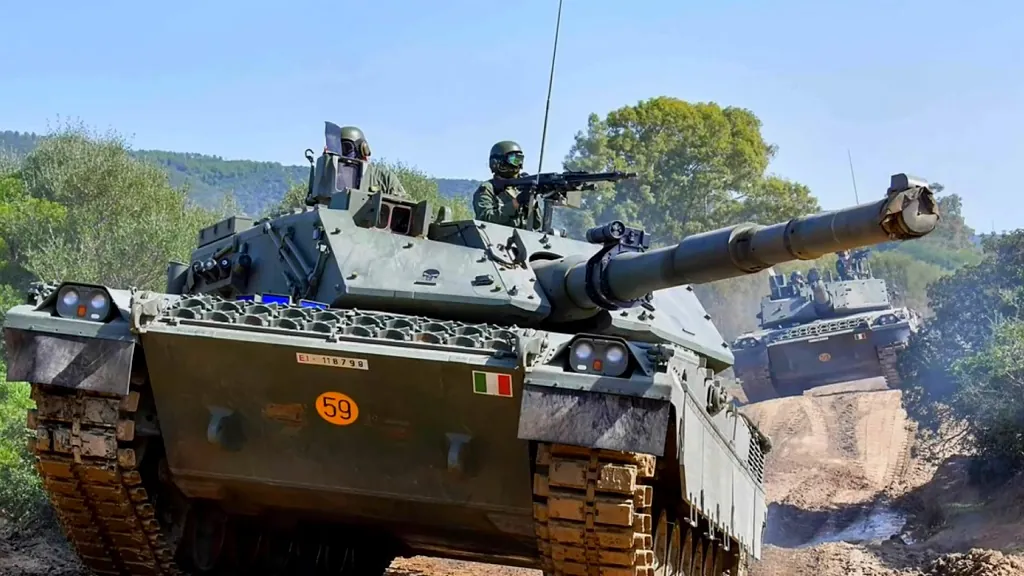

Italy holds the tenth position, with a balanced military force that includes strong aerial and naval capabilities.
Commitment to NATO and its modernized forces maintains its ranking in global military power.
- Steady Defense Budget – Italy allocates $31.6 billion to its defense needs, with a plan to increase it up to $38.5 billion by 2028.
- Diverse Naval Assets – Italy’s naval forces include aircraft carriers and submarines.
- NATO Commitment – Italy’s role in NATO shapes its defense priorities.
| Defense Budget | $31.6 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 289,000 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 850 (fighters, bombers, helicopters) |
| Aircraft Carriers | 2 |
| Warships | 30, including frigates and destroyers |
| Submarines | 8 |
| Active Tanks | 200 |
| Missile Systems | Short-range air defense systems |
Where is Brazil on This List?
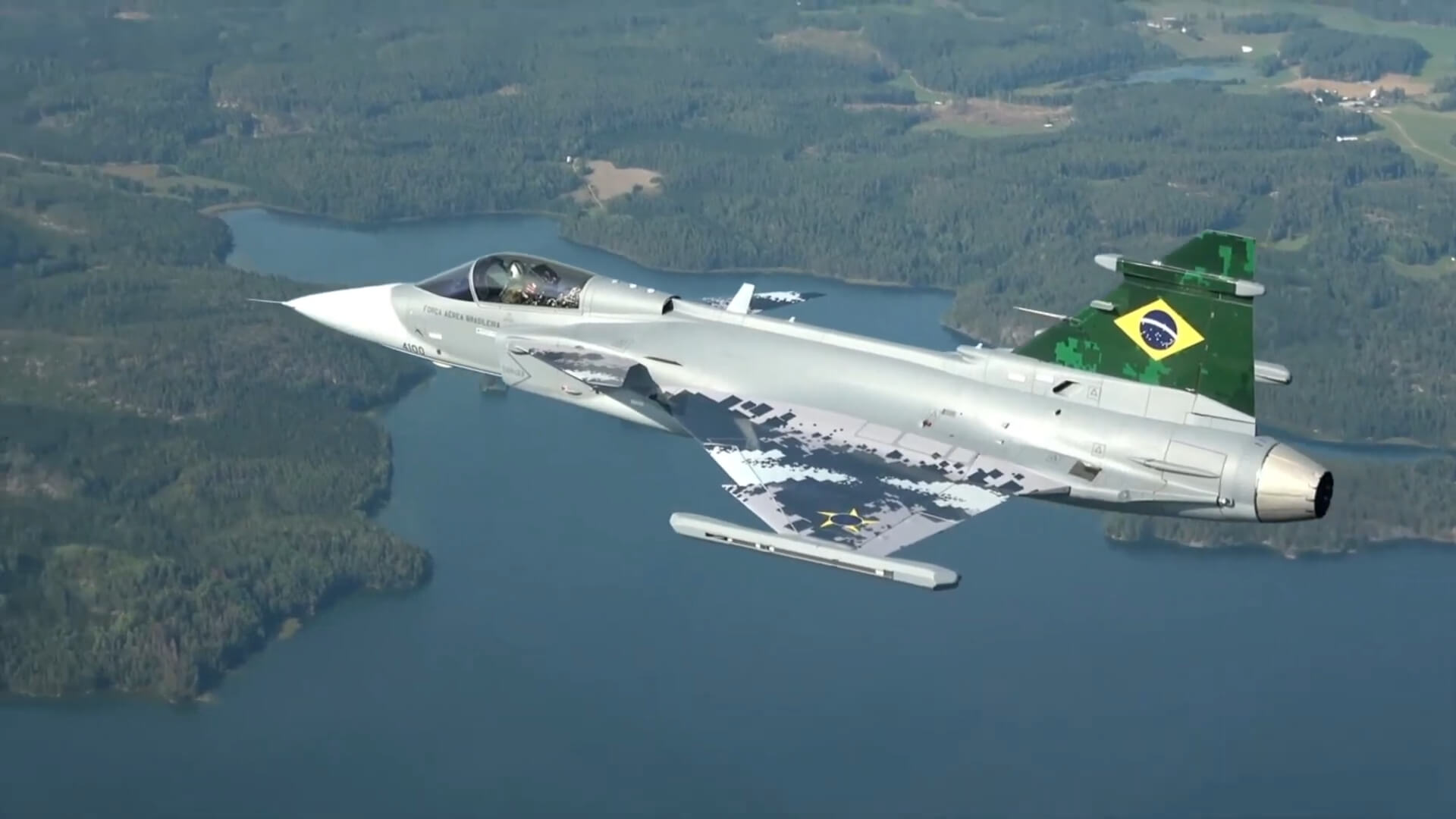

Brazil ranks 12th in the global military strength list for 2025, holding the title of the strongest military in South America.
Focus on regional security, a prominent defense budget, and a well-equipped military make it a dominant force within Latin America.
Brazil holds 11th place among the strongest navies in the world.
- Largest Defense Budget in South America – Brazil allocates $24.75 billion to its defense, surpassing other countries in the region.
- Strong Army and Naval Force – Brazil maintains a well-rounded military with a focus on land and naval strength.
- Regional Influence – As the most populous country in South America, Brazil’s military power influences stability across the continent.
| Defense Budget | $24.75 billion |
| Total Military Personnel | 2,101,500 (all branches) |
| Aircraft Fleet | 715 (fighters, helicopters, transport) |
| Warships | 108, including frigates and patrol ships |
| Submarines | 7, including diesel-electric models |
| Active Tanks | 439 |
| Missile Systems | Short-range missiles for defense |
Challenges with Crime and Urban Security
Organized crime and violence remain pressing issues in cities like Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo.
The military sometimes plays a role in combating these issues, as police and other security forces frequently request assistance to address high levels of gang activity and violent crime in these populous areas.
FAQs
Will Turkey join BRICS?
Turkey has shown interest in joining BRICS, but it has not become a member yet. Focus is often on balancing relations with both Western countries and groups like BRICS, so any potential membership could depend on changing global relationships.
Does Brazil work with NATO?
No, Brazil is not part of NATO and doesn’t have direct ties with the alliance. NATO mainly focuses on Europe and North America, while Brazil focuses on South America. However, Brazil cooperates with other countries, including some NATO members, on specific security issues.
Can NATO and BRICS countries cooperate?
Yes, while NATO and BRICS have different goals, they can cooperate on issues like trade, climate change, and counter-terrorism. Some NATO countries have connections with BRICS members, which helps in forming bridges between the two groups on certain global issues.
What is the difference between active and reserve military personnel?
Active personnel are full-time members of the military, ready for deployment at any time, while reserve personnel are part-time and can be called up during emergencies. Countries with large reserve forces, like the United States and Russia, have added flexibility in scaling up their military strength when needed.
Last Words
Military strength in 2025 reveals each country’s approach to preparing for future security needs. Some nations focus on advanced technology, while others rely on large forces or regional influence.
The rankings of the strongest armies highlight the commitment that each nation places on defense and stability.
As new challenges emerge, positions may shift, but every country on this list remains prepared for the road ahead.
How the Strongest Armies Were Ranked
The ranking uses the 2025 Global Firepower Index. It looks at defense budget, total number of troops, warplanes, warships, tanks, missile systems, and overall military technology.
A lower Power Index score means more military power. Countries that can send forces overseas, respond fast, and maintain strong defense across land, sea, and air rank higher.