
Europe will begin Daylight Saving Time (DST) on Sunday, March 30, 2025, when clocks will move forward by one hour at 1:00 UTC. This shift means that in Central European Time (CET), clocks will jump from 2:00 AM to 3:00 AM.
Countries that follow DST will stay on this schedule until Sunday, October 26, 2025, when clocks will move back by one hour at 1:00 UTC.
Which Countries in Europe Observe DST?
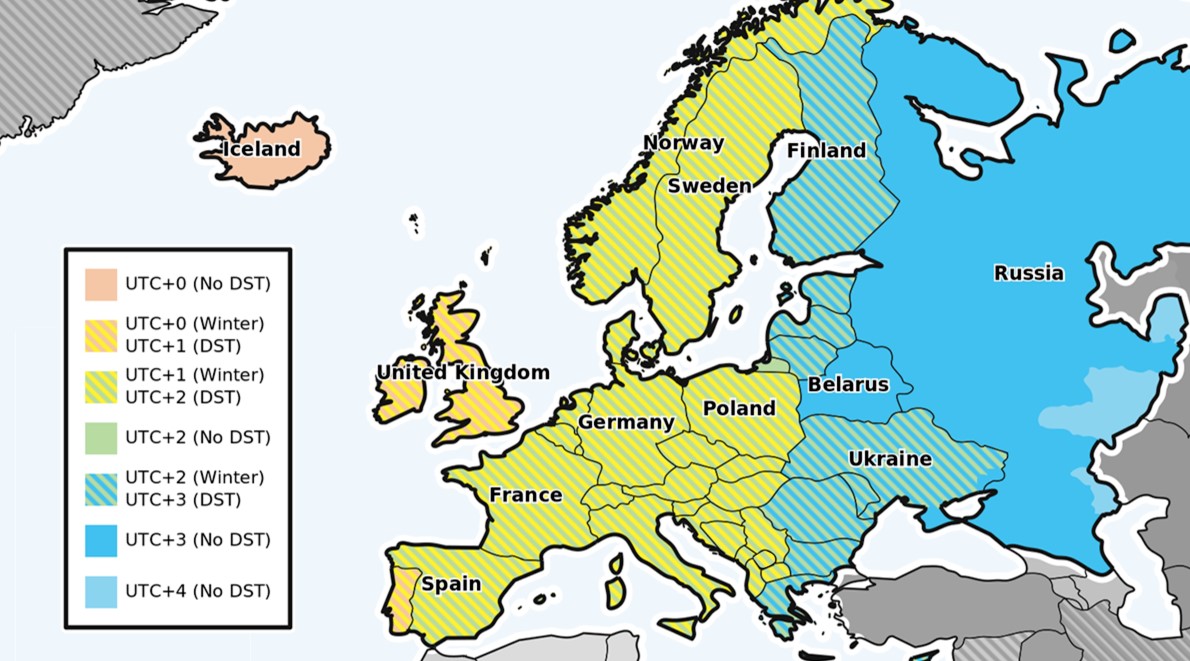
Most European nations adjust clocks twice a year, but some do not participate. Here is a breakdown:
Countries That Follow DST
- Germany, France, Spain, Italy, Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, Denmark
- Poland, Czech Republic, Hungary, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Portugal
- Ireland, United Kingdom, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Greece, Romania, Bulgaria
Countries That Do Not Follow DST
- Iceland keeps the same time all year.
- Russia, Belarus, Turkey do not move clocks forward.
Why Does Europe Use Daylight Saving Time?

The main reason for DST is to extend daylight hours in the evening, reducing energy use and allowing people to spend more time outdoors.
Many argue that it improves daily life, but some believe it causes sleep problems and disrupts routines.
Will Europe End Daylight Saving Time?
The European Union debated ending DST, but no agreement has been reached. Some countries want to keep the time change, while others prefer permanent standard time or daylight time. Until officials make a final decision, DST will continue.
How to Prepare for the 2025 Time Change
- Go to bed earlier the night before the change to avoid feeling tired.
- Adjust clocks manually if your devices do not update automatically.
- Check travel schedules since flights and trains follow UTC-based timing.
- Be aware of time differences if contacting people in non-DST countries.
How Does Brazil Handle Daylight Saving Time?
Brazil does not observe Daylight Saving Time anymore. The government permanently abolished DST in 2019, citing concerns about its effects on sleep patterns and health. Studies showed that shifting clocks disrupted people’s biological rhythms, leading to lower productivity and increased health issues.
Before that decision, Brazil used DST for decades, with the southern states adjusting clocks due to longer daylight hours in summer. Northern regions, closer to the equator, never used it because daylight variation was minimal.
















